
Reviewed and Updated: August 5th 2024
Nutrient absorption is a complex process influenced by various factors, from our dietary choices to our lifestyle habits. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies to enhance absorption can significantly impact our overall well-being. In this blog post, we'll explore the science behind nutrient absorption and provide practical tips to help you make the most of every bite.
How Nutrients Get Absorbed
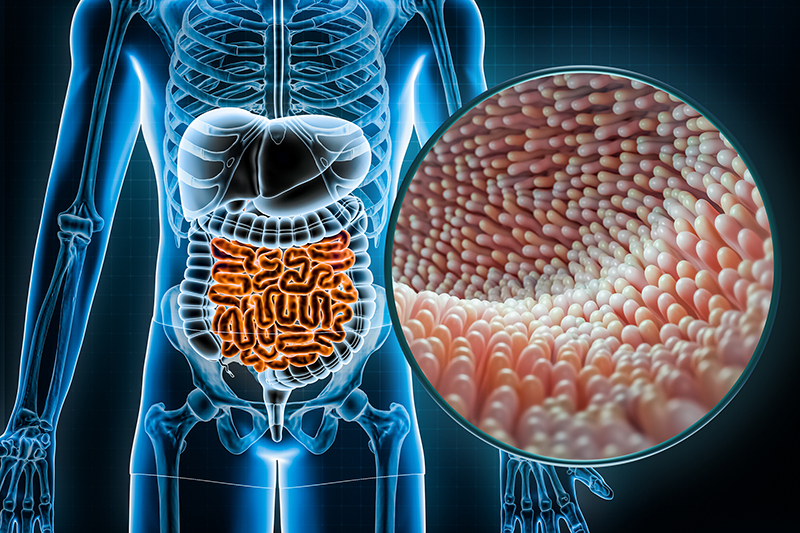
While digestion begins in the mouth, nutrient absorption primarily occurs in the small intestine, which is lined with millions of finger-like projections called villi . These villi play a vital role in absorbing nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, facilitating their transport into the bloodstream for distribution to various tissues and organs.
Factors That Can Negatively Affect Nutrient Absorption
Several factors can negatively affect nutrient absorption, compromising the body's ability to utilize them effectively. Certain medical conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) can impair nutrient absorption by damaging the intestinal lining or affecting enzyme production. When malabsorption occurs, our body has a hard time absorbing things like fats, protein, vitamins, and sugars.
Certain medications like antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors ( a type of acid reflux medication), and antacids may interfere with nutrient absorption by altering gut bacteria or reducing stomach acid levels. Also, age-related changes in digestive function and lifestyle factors such as stress, alcohol consumption, and smoking can further exacerbate nutrient absorption issues.
Smart Cooking Choices

Certain cooking methods can help preserve the integrity of nutrients, ensuring they remain bioavailable and ready for absorption.
For instance, steaming, microwaving, and stir-frying are gentle cooking techniques that can help retain water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins. On the other hand, boiling and prolonged exposure to high heat may lead to nutrient loss. By choosing cooking methods that minimize nutrient breakdown, you can maximize the nutritional value of your meals.
Food Combinations That Aid in Absorption

Pairing vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits or bell peppers, with non-heme iron-rich plant sources like spinach or lentils can notably improve the absorption of iron.
Similarly, incorporating healthy fats, such as those found in avocados or nuts, with fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, E, and K from vegetables or fruits, can enhance their absorption. Additionally, more calcium gets absorbed from food when activated vitamin D is in the body to maintain healthy bones.
Combining sources of beta-carotene, found in colorful vegetables like carrots or sweet potatoes, with a small amount of healthy fat like olive oil can also enhance its conversion to vitamin A in the body. These thoughtful food pairings can maximize the nutritional benefits of the diet, ensuring efficient absorption and utilization of vital nutrients for optimal health.
The Truth About Frozen Produce
Frozen foods often receive a bad rap, but they can actually be a convenient and nutritious option. When fruits and vegetables are frozen, they are typically picked at peak ripeness and then quickly frozen, preserving their nutritional content. In fact, freezing can sometimes retain more nutrients compared to fresh produce that has been sitting on shelves for an extended period.
Additionally, frozen foods are often processed shortly after harvesting, which helps to lock in vitamins and minerals. Frozen produce is great for smoothies, quick dinners, and added to soups. Incorporating a variety of frozen fruits, vegetables, and other frozen foods into your diet can contribute to meeting your daily nutrient needs conveniently.
Compare this to fresh produce that has to get picked when it’s less mature and sits on shelves losing quality by the day.
The Bottom Line
By understanding the science behind nutrient absorption and implementing strategies to enhance it, you can maximize the full potential of your diet for optimal health. From choosing nutrient-dense foods to adopting smart cooking techniques, small changes can yield significant benefits.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease.








Validate your login
Sign In
Create New Account